World War II is one of the most significant events in modern history, yet many of us are surprisingly unfamiliar with some of its basic details. The war shaped the world we live in today, but you’d be surprised how many people, even in the U.S., struggle to answer simple questions about it. From key battles to influential figures, this period is packed with important moments that defined global politics, yet they often slip under the radar for many.
It’s not that people don’t care about history, but the vast scale and complexity of World War II can make it tough to keep track of all the facts. In this article, we’ve put together 20 questions that might stump even the most well-versed history buffs. If you think you know your WWII facts, give it a try—you might be surprised by what you remember, and what you didn’t quite catch in school.
Who was the British Prime Minister during most of WWII?
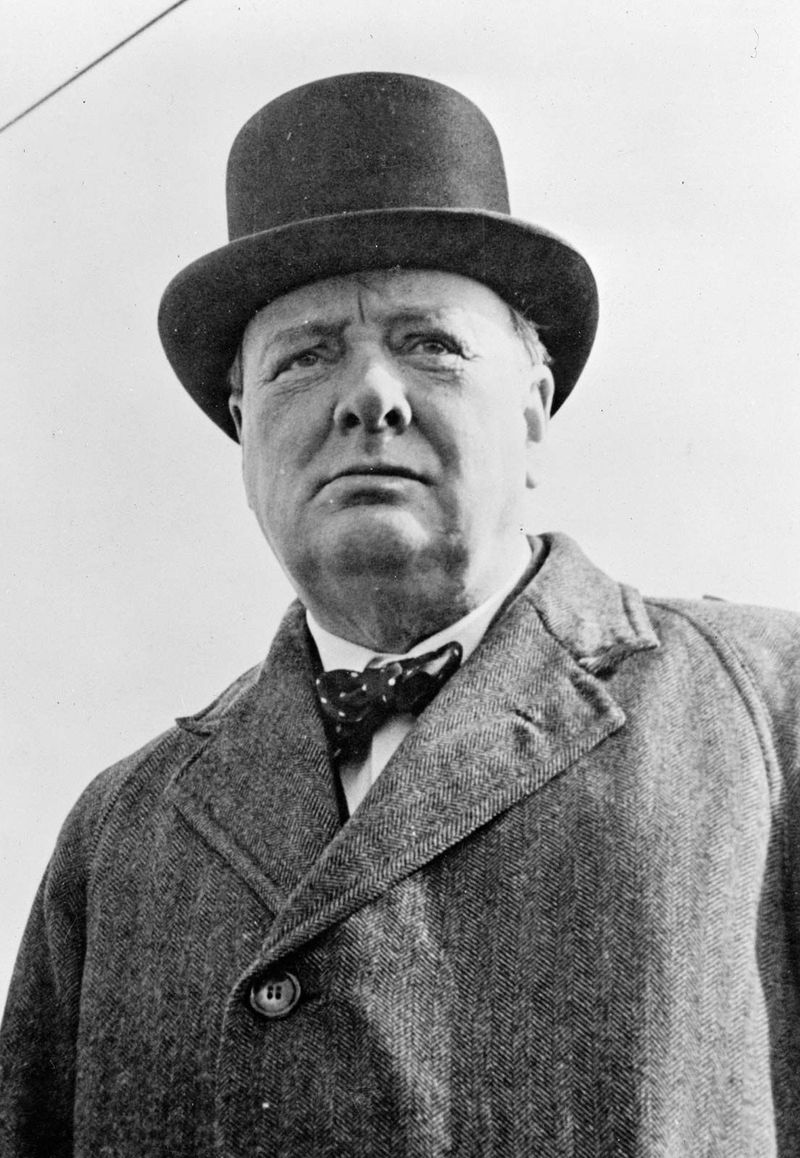

Winston Churchill, known for his leadership during WWII, served as the British Prime Minister from 1940 to 1945. His speeches invigorated British forces and citizens during the bleakest times of the war. Churchill’s resilience and determination became emblematic of the British wartime spirit.
His strategic decisions, including forging alliances with the United States and Soviet Union, were crucial in countering Nazi aggression. Despite facing initial criticism, his efforts helped turn the tide in favor of the Allies.
Churchill’s legacy continues to inspire, reminding us of the importance of steadfast leadership in times of crisis.
What event triggered the United States’ entry into WWII?

The attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, marked the catalyst for the United States’ entry into World War II. The Japanese surprise assault targeted the naval base in Hawaii, aiming to neutralize the US Pacific Fleet.
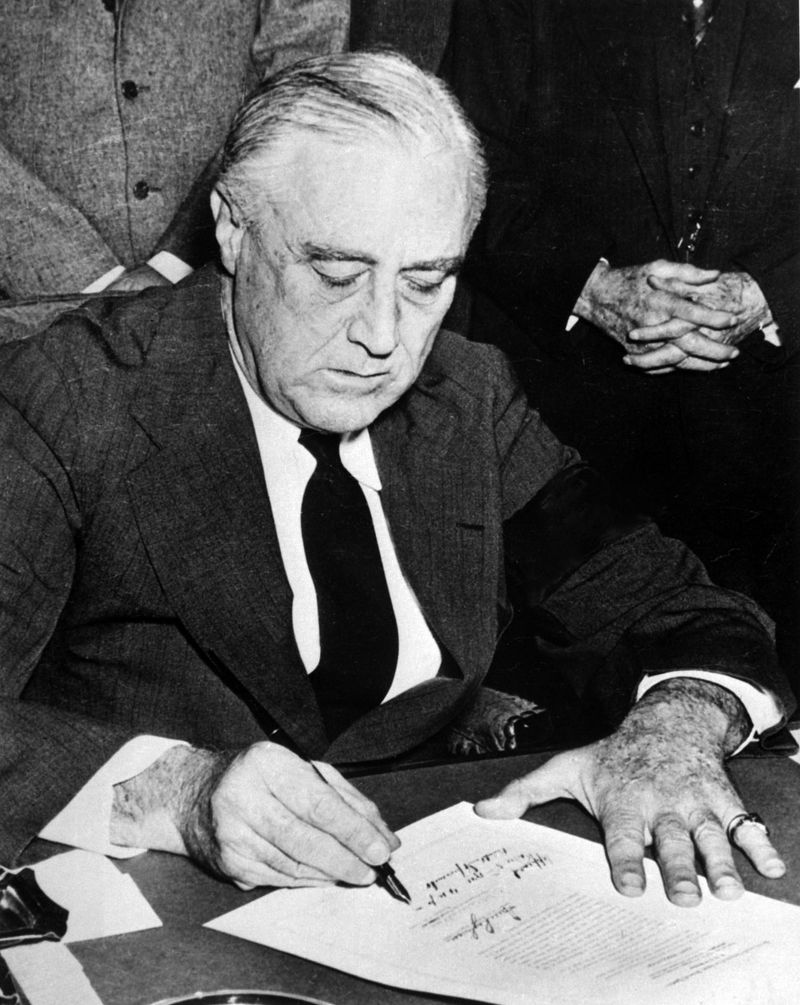
This event shocked the American public, transforming isolationist sentiments overnight. Following the attack, President Franklin D. Roosevelt declared it “a date which will live in infamy” and led America into active participation in the war.
Pearl Harbor remains a significant historical event, highlighting the impact of unexpected aggression and the resilience required to respond effectively.
What was the largest amphibious invasion in history?
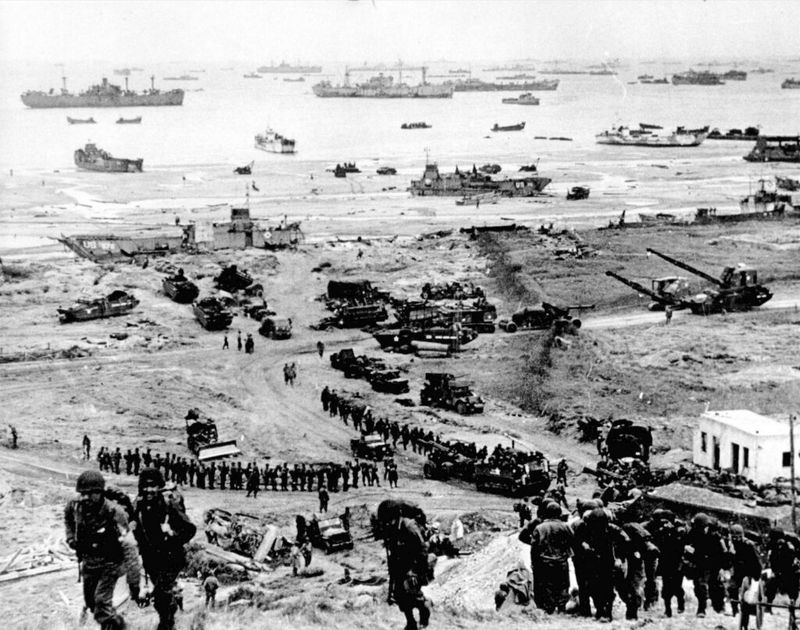

The largest amphibious invasion in history occurred on D-Day, June 6, 1944, when Allied forces stormed the beaches of Normandy, France. This pivotal operation aimed to liberate Western Europe from Nazi occupation.
Led by General Dwight D. Eisenhower, the invasion involved thousands of ships, aircraft, and troops from multiple Allied nations. The sacrifices made on that day were immense, but the operation was a turning point in the war.
D-Day exemplifies the courage and cooperation required to execute such a complex military campaign, underscoring the importance of unity in overcoming formidable challenges.
Who was the President of the United States during most of WWII?
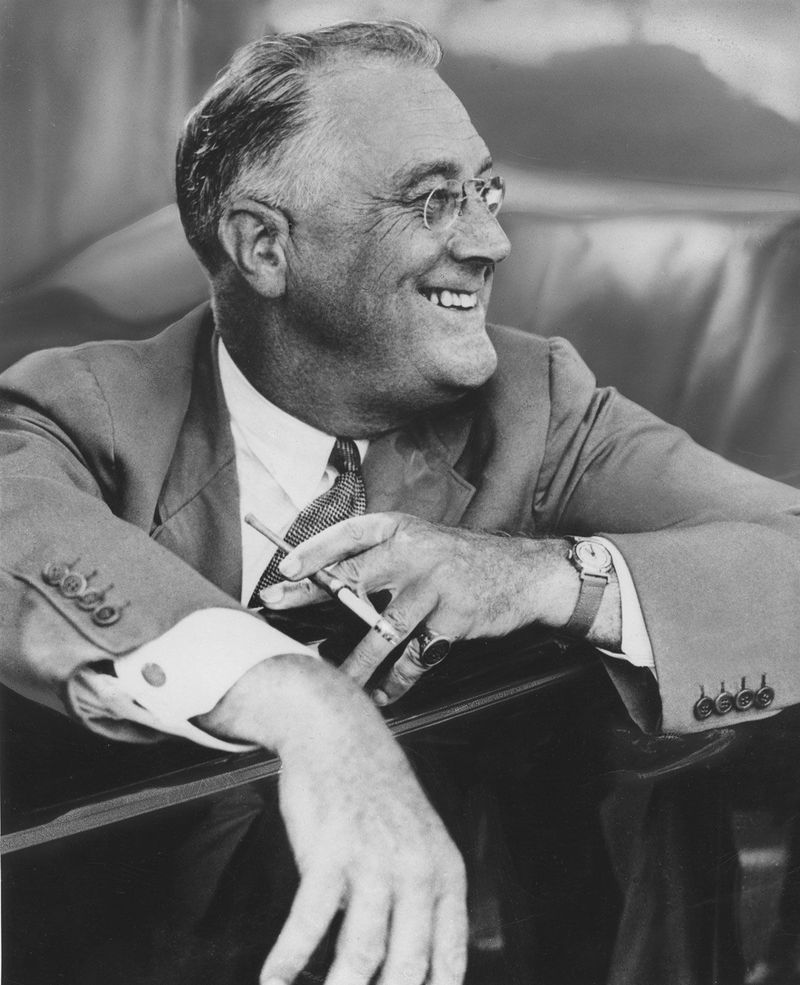

Franklin D. Roosevelt, often referred to as FDR, served as the President of the United States during most of World War II. His leadership spanned from 1933 until his death in 1945.
Roosevelt’s policies and diplomatic efforts were instrumental in shaping the Allied strategy against the Axis powers. He was a key figure in the establishment of the United Nations, striving for global peace post-war.
FDR’s ability to lead the nation through both the Great Depression and WWII illustrates his profound impact on American history, highlighting the importance of visionary leadership.
What was the Holocaust?
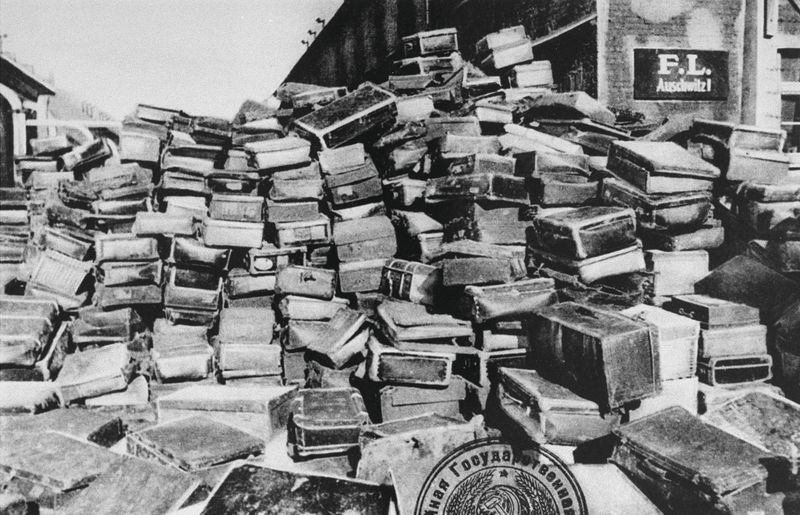

The Holocaust was the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews by the Nazi regime and its collaborators. Occurring between 1941 and 1945, it remains one of history’s darkest chapters.
The Nazis targeted various groups, including Romani people, disabled individuals, Poles, Soviet POWs, and others deemed “undesirable.” This genocide was driven by an ideology of racial superiority and anti-Semitism.
Understanding the Holocaust is crucial to preventing future atrocities and fostering a world committed to justice and human rights. This tragic event emphasizes the need for vigilance against hatred.
What was the significance of the Battle of Stalingrad?
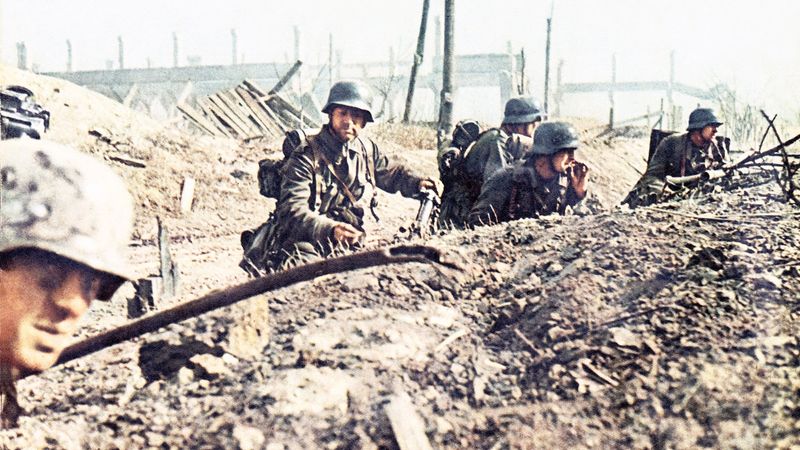

The Battle of Stalingrad, fought from 1942 to 1943, was a critical turning point in World War II. This brutal confrontation between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union marked a decisive shift in the war’s momentum.
The fierce urban warfare and harsh winter conditions led to massive casualties on both sides. Soviet victory at Stalingrad halted the German advance into the Soviet Union, boosting Allied morale and weakening Axis forces.
This battle exemplifies resilience and strategic prowess, showcasing the tenacity needed to overcome dire circumstances and alter the course of history.
Which country was invaded to start WWII?
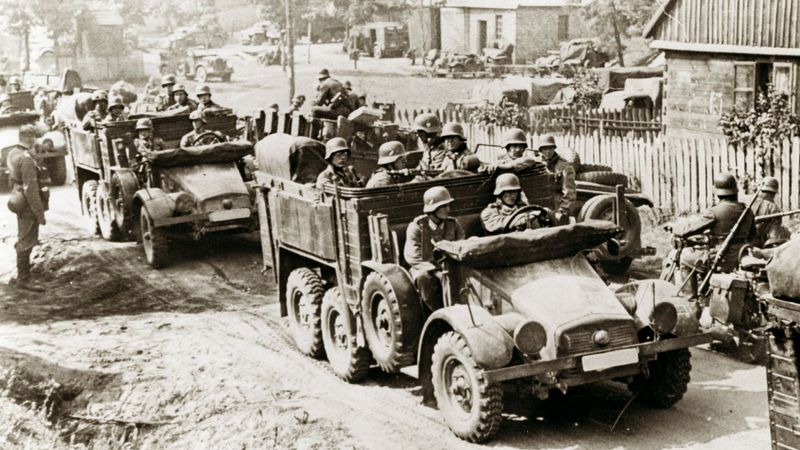

World War II officially began with the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany on September 1, 1939. This aggressive move violated international treaties and prompted Britain and France to declare war on Germany.
The invasion demonstrated Germany’s blitzkrieg tactics, characterized by rapid and overwhelming military force. Poland’s resistance was valiant but ultimately overwhelmed by the German advance.
The fall of Poland set the stage for further Axis expansion and highlighted the need for international unity and swift action in the face of aggression. It serves as a reminder of the consequences of unchecked militarism.
Who were the Axis powers?
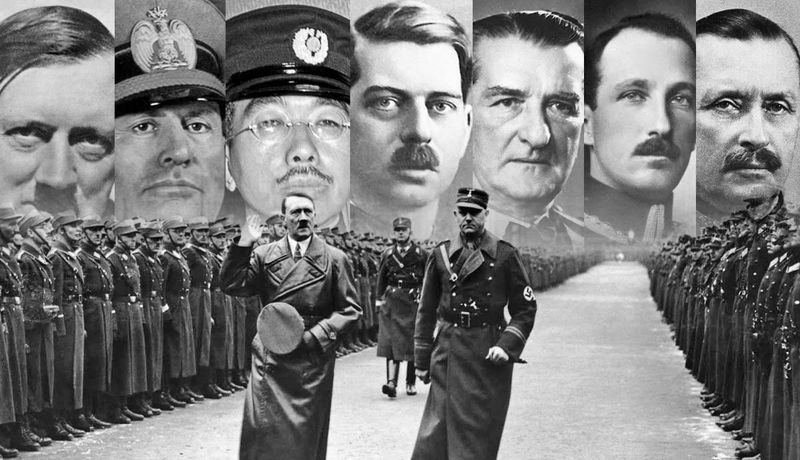

The Axis powers in World War II were primarily composed of Germany, Italy, and Japan. These nations formed a military alliance with the goal of expanding their territories and establishing dominance.
Germany, under Adolf Hitler, sought to create a vast empire across Europe. Italy, led by Benito Mussolini, aimed to revive the glory of the Roman Empire, while Japan pursued expansion in Asia and the Pacific.
The Axis powers’ aggressive actions and expansionist ambitions led to widespread conflict and devastation, underscoring the dangers of totalitarian regimes and unchecked imperialism.
What was the Manhattan Project?
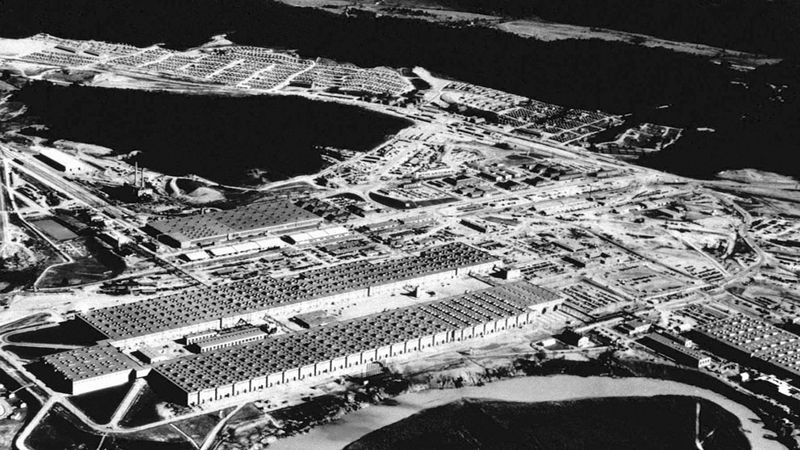

The Manhattan Project was a top-secret initiative during World War II that led to the development of the atomic bomb. Initiated in 1942, it involved leading scientists and researchers working under intense pressure.
The project culminated in the successful detonation of the first nuclear weapon in July 1945, a pivotal moment in military history. The subsequent bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki forced Japan’s surrender, effectively ending the war.
The Manhattan Project raises ethical questions about nuclear warfare and highlights the profound impact of scientific advancements on global security and diplomacy.
Who was Anne Frank?
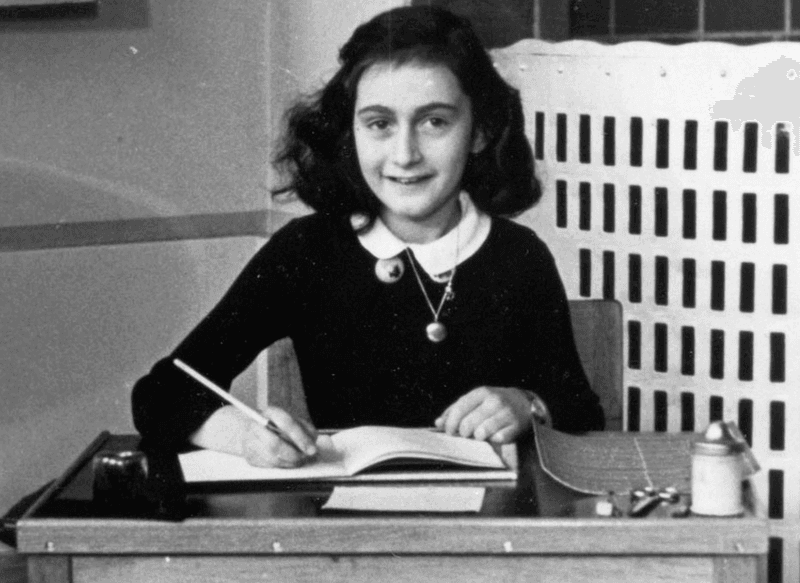

Anne Frank, a Jewish teenager, became one of the most discussed Holocaust victims through her diary. Living in hiding in Amsterdam during the Nazi occupation, her writings document the fears and hopes of life under persecution.
Her diary provides a poignant, personal perspective on the hardships faced by Jews during the war. Sadly, Anne and her family were eventually discovered and deported to concentration camps, where she perished.
Anne Frank’s legacy endures through her diary, a powerful testament to the human spirit and a reminder of the horrors of discrimination and intolerance.
What was Operation Barbarossa?
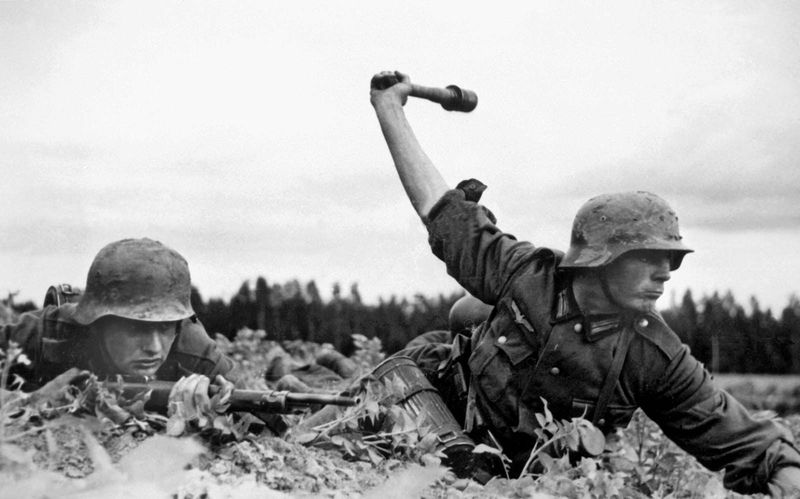

Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Nazi Germany’s invasion of the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941. It was the largest military operation in history, characterized by its devastating scale and ambition.
The offensive aimed to conquer Soviet lands swiftly, but underestimated Soviet resilience and the harsh winter. The invasion eventually stalled, marking a significant setback for Germany.
Operation Barbarossa highlights the perils of overreaching military campaigns and the resilience required to withstand aggression. It remains a crucial study in strategic miscalculations and the impact of environmental factors on warfare.
What was the purpose of the Nuremberg Trials?
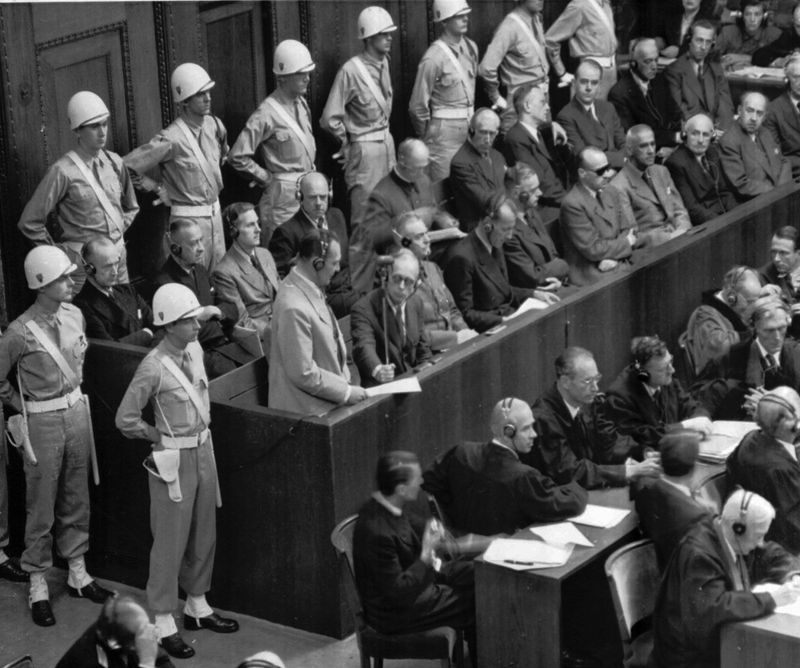

The Nuremberg Trials, held after World War II, were a series of military tribunals that aimed to bring Nazi war criminals to justice. Conducted from 1945 to 1946, they represented a landmark in international law.
These trials prosecuted prominent leaders of Nazi Germany for crimes against humanity, war crimes, and genocide. The proceedings established precedents for dealing with war crimes and human rights violations.
The Nuremberg Trials underscore the importance of accountability and the international community’s commitment to justice, setting a foundation for future legal frameworks in addressing crimes against humanity.
What was the significance of the Battle of Midway?
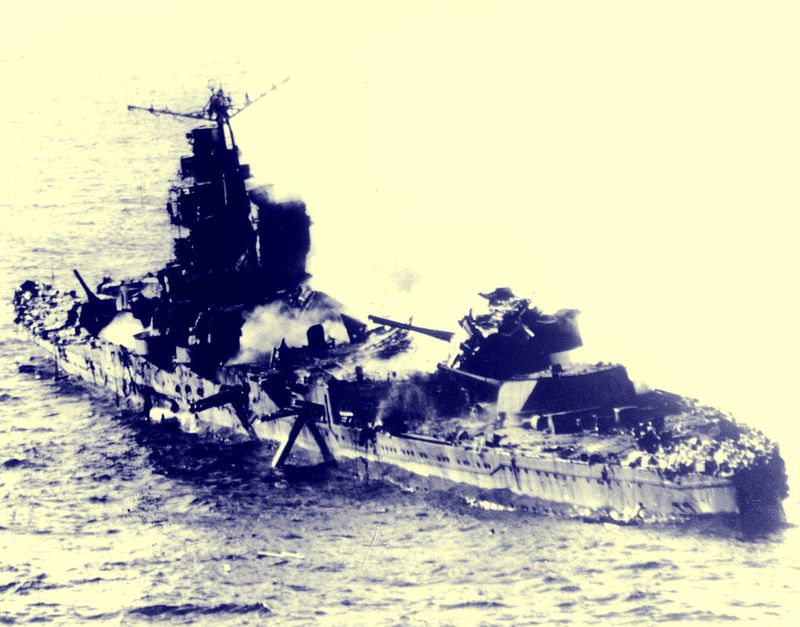
The Battle of Midway, fought in June 1942, was a significant naval battle in the Pacific Theater of World War II. This decisive encounter marked a turning point in the war against Japan.
American forces, utilizing intelligence breakthroughs, successfully ambushed and defeated the Japanese fleet, inflicting irreparable damage. The victory halted Japanese expansion and shifted the balance of power in the Pacific.
The Battle of Midway demonstrates the strategic importance of intelligence and naval power, shaping the course of WWII in favor of the Allies. It remains a testament to effective military planning and execution.
What were the internment camps in the United States during WWII?
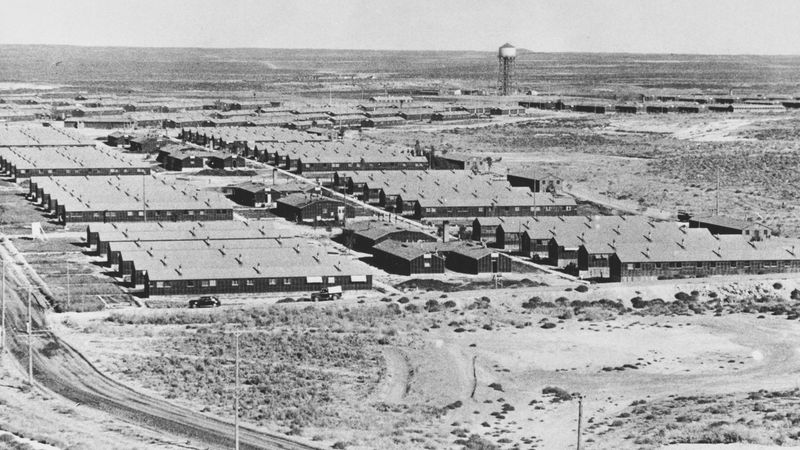

During World War II, the United States established internment camps for Japanese Americans, driven by wartime hysteria and racial prejudice. Over 120,000 individuals, many of whom were U.S. citizens, were forcibly relocated and confined.
These camps, often located in remote areas, subjected internees to harsh conditions and stripped them of their civil liberties. The internment remains a dark chapter in American history, reflecting the consequences of fear-driven policies.
Acknowledging this injustice is essential for promoting civil rights and ensuring that similar violations of freedom never occur again. It serves as a poignant lesson in vigilance.
Who was the Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force in Europe?
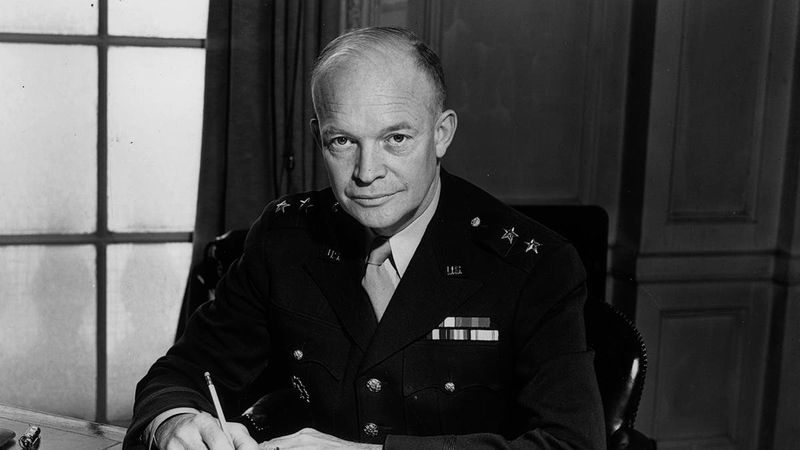

General Dwight D. Eisenhower served as the Supreme Commander of the Allied Expeditionary Force in Europe during World War II. His leadership was pivotal in planning and executing major operations, including the D-Day invasion.
Eisenhower’s ability to coordinate diverse Allied forces showcased his diplomatic and strategic acumen. His efforts played a vital role in the liberation of Europe from Nazi control.
Eisenhower’s legacy extends beyond his military achievements, as he later became the 34th President of the United States, illustrating the profound impact of military leadership on global history and politics.
What was the significance of the Siege of Leningrad?
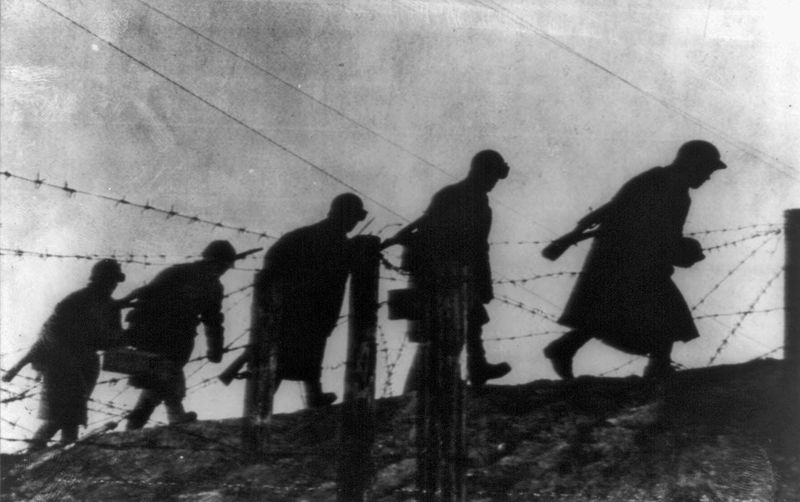

The Siege of Leningrad, lasting from 1941 to 1944, was one of the longest and most devastating sieges in history. Nazi forces encircled the Soviet city, aiming to starve it into submission.
Despite severe hardships, including famine and extreme cold, the city’s defenders and inhabitants displayed remarkable resilience. The eventual lifting of the siege marked a significant turning point on the Eastern Front.
The Siege of Leningrad exemplifies human endurance and the spirit of resistance, underscoring the profound impact of warfare on civilian populations and the enduring strength of community determination.
What was VE Day?
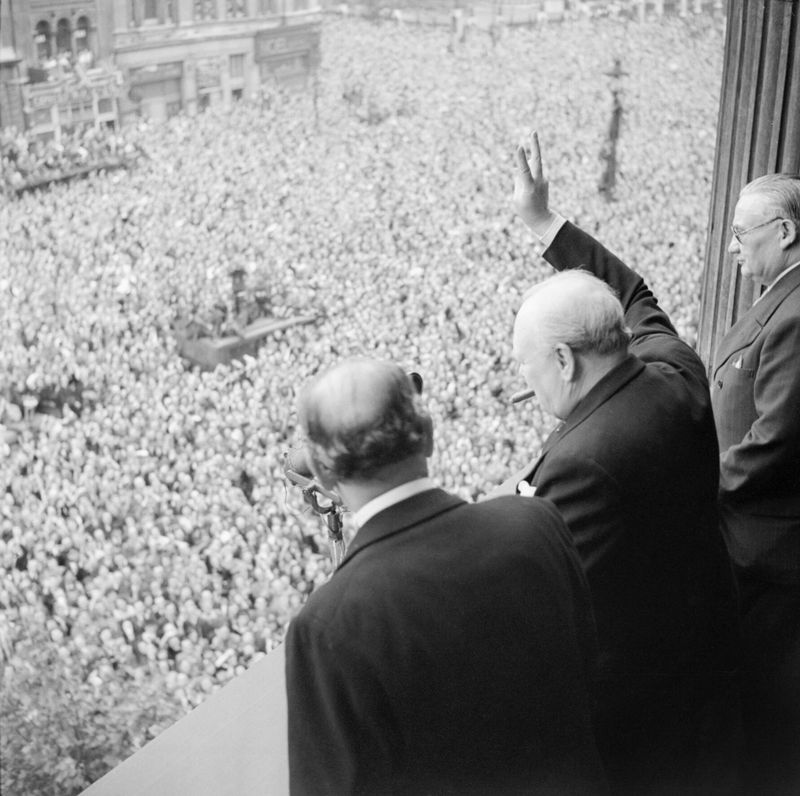

VE Day, or Victory in Europe Day, celebrated on May 8, 1945, marked the formal acceptance of Nazi Germany’s unconditional surrender, ending World War II in Europe. This day is commemorated with jubilant celebrations across Allied nations.
VE Day symbolizes the triumph of freedom and justice over tyranny and oppression. It honors the sacrifices made by countless individuals who contributed to the defeat of the Axis powers.
The celebrations of VE Day remind us of the enduring quest for peace and the importance of collective efforts in overcoming global challenges. It continues to inspire hope and unity.
What was the Bataan Death March?
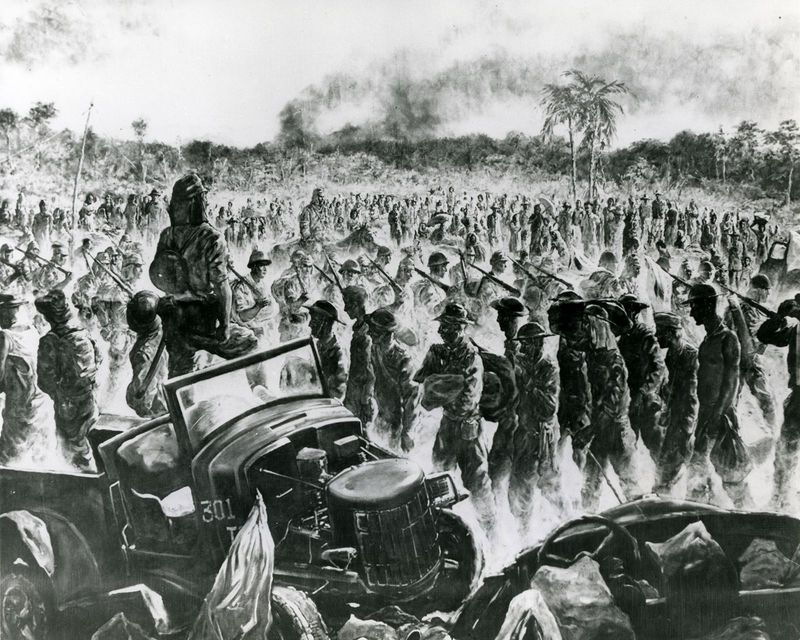

The Bataan Death March occurred in 1942 after the surrender of Allied forces in the Philippines to the Japanese. Forced to march over 60 miles in brutal conditions, thousands of prisoners of war suffered severe abuse and deprivation.
The march resulted in significant loss of life, highlighting the harsh realities and brutality of war. Survivors faced further hardships in Japanese internment camps.
The Bataan Death March is a somber reminder of the resilience of those who endured and the need for accountability in warfare. It underscores the importance of remembering past atrocities to prevent future ones.
What was Operation Overlord?
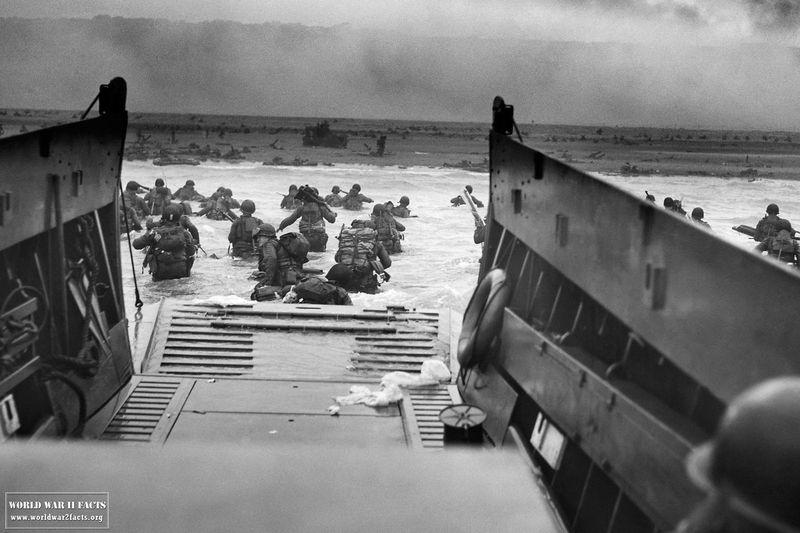

Operation Overlord was the code name for the Allied invasion of Nazi-occupied Western Europe, beginning with the D-Day landings on June 6, 1944. This operation was a monumental effort involving extensive planning and coordination.
The success of Operation Overlord was pivotal in liberating Europe from Nazi control. It demonstrated the power of collaboration among Allied forces and the importance of strategic innovation.
Operation Overlord highlights the courage and determination required to confront tyranny and restore peace. The operation’s success laid the groundwork for the eventual defeat of Nazi Germany, shaping the post-war world order.
What was the significance of the Yalta Conference?
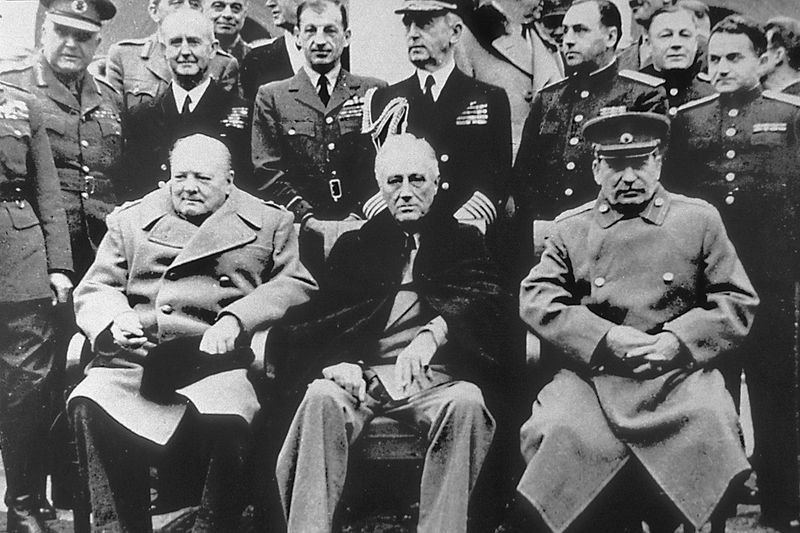

The Yalta Conference, held in February 1945, brought together Allied leaders Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin to discuss post-war plans. This meeting aimed to ensure peace and stability in Europe following WWII.
Key agreements included the division of Germany into occupation zones and the establishment of the United Nations. However, some decisions led to tensions that contributed to the Cold War.
The Yalta Conference exemplifies the complexities of diplomacy and the challenges of forging lasting peace. It underscores the importance of collaborative problem-solving and the need to address both immediate and long-term global issues.
